refractometer definition in physics|refractometer uses in laboratory : manufacturers The changing of a light ray’s direction (loosely called bending) when it passes through variations in matter is called refraction. Refraction is responsible for a tremendous range of optical phenomena, from the action of lenses to voice . web95K Followers, 310 Following, 1,326 Posts - See Instagram photos and videos from Panobianco Academia Oficial (@panobiancoacademia)
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBTutorial para acceder a la AcademiaOliverVelez.com. Si tienes alguna duda escribe a [email protected].
Refraction, in physics, the change in direction of a wave passing from one medium to another caused by its change in speed. For example, . Refraction is a phenomenon when a ray of light traveling through a medium changes (bends) its direction upon entering into another medium. The two media are separated by an interface through which the ray enters the . Refraction is the change in direction of the wave as it passes from one medium to another. Understand the law governing the refraction of light, its applications and more. A refractometer is a scientific instrument used to gauge a liquid's index of refraction. The refractive index is determined by placing a liquid sample on a prism and allowing light to pass through them to create a visible .
The changing of a light ray’s direction (loosely called bending) when it passes through variations in matter is called refraction. Refraction is responsible for a tremendous range of optical phenomena, from the action of lenses to voice . Refraction is the change in direction of a wave caused by a change in speed as the wave passes from one medium to another. Snell's law describes this change.
The ray nature of light is used to explain how light refracts at planar and curved surfaces; Snell's law and refraction principles are used to explain a variety of real-world phenomena; .Refraction is the change of direction of wave that occurs when its speed changes. Angle formed by the incident ray with the normal is called as angle of incidence (i). Angle formed by the refracted ray with the normal is called as .
iphone 6s vs 6s plus drop test
The reflection and refraction of light explains how people see images, colour and even optical illusions. Part of Physics (Single Science) Waves Save to My Bitesize Remove from My BitesizeSummary Refraction is the change in direction of a wave caused by a change in wave speed.. An interface is the boundary between two different media.. or two regions of a medium with different characteristics such as. density (which is often related to temperature) concentration of solute (salinity, for example)Speed of Light. The speed of light c not only affects refraction, it is one of the central concepts of Einstein’s theory of relativity. The speed of light varies in a precise manner with the material it traverses. It makes connections between .Refraction is a phenomenon that is exhibited by wave when it travels from one medium to another, for example, when light travels from air to glass or vice versa. Refraction can be also be seen when water waves move from deeper into shallower water. A. Refraction. Consider figure 1 that shows the refraction of light when it travels from air to .
The associated angles are called the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction. Later, we apply Snell’s law to some practical situations. Dispersion is defined as the spreading of white light into the wavelengths of which it is composed. This happens because the index of refraction varies slightly with wavelength. Refractometer FAQs What is a Refractometer? A refractometer is a simple instrument used for measuring concentrations of aqueous solutions such as gases, liquids, and translucent solids. Different types of refractometers are available depending on the application. Refractometers can be handheld, compact, benchtop, Abbe, and Brix as well as different .Find the index of refraction for medium 2 in Figure \(\PageIndex{1a}\), assuming medium 1 is air and given that the incident angle is 30.0° and the angle of refraction is 22.0°. Strategy. The index of refraction for air is taken to be 1 in most cases (and up to four significant figures, it is 1.000). Thus, \(n_1=1.00\) here.Refractometry is the analytical method of measuring substances' refractive index (one of their fundamental physical properties) in order to, for instance, assess their composition or purity.A refractometer is the instrument used to measure refractive index ("RI"). Although refractometers are best known for measuring liquids, they are also used to measure gases and solids, such .
Light - Reflection, Refraction, Physics: Light rays change direction when they reflect off a surface, move from one transparent medium into another, or travel through a medium whose composition is continuously changing. The law of reflection states that, on reflection from a smooth surface, the angle of the reflected ray is equal to the angle of the incident ray. (By .
Refraction of light. Refraction occurs when light passes a boundary between two different transparent materials. At the boundary, the rays of light change direction. This change in direction depends on the difference in density between the two media:. From less dense to more dense (e.g air to glass), light bends towards the normal From more dense to less dense (e.g. .
Definition: REFRACTION. The changing of a light ray’s direction (loosely called bending) when it passes through variations in matter is called refraction. . (University of Auckland) and Manjula Sharma (University of Sydney). This work is licensed by OpenStax University Physics under a Creative Commons Attribution License (by 4.0). This page .A refractometer is a scientific instrument used to measure the refractive index of different materials – a value indicating how much the phase velocity of light is smaller compared with propagation in vacuum. Various refractometer types allow measurements in liquid, solid, or gaseous samples. Refractometers have a long history and a wide range of applications in .Learn about refraction, ray diagrams and how convex lenses bend light rays with this guide for KS3 physics students aged 11-14 from BBC Bitesize. Transmission can involve refraction but is not exactly the same; For the process to count as transmission, the wave must pass through the material and emerge from the other side . Ashika graduated with a first-class Physics degree from Manchester University and, having worked as a software engineer, focused on Physics education, creating .
The ray nature of light is used to explain how light refracts at planar and curved surfaces; Snell's law and refraction principles are used to explain a variety of real-world phenomena; refraction principles are combined with ray diagrams to explain why lenses produce images of objects.
A refractometer is a device used to measure the refractive index (n) of a substance. In this article, we discuss what a refractometer is and how it works, the different types available and their applications in the food industry. .Refraction of Waves. Reflection involves a change in direction of waves when they bounce off a barrier. Refraction of waves involves a change in the direction of waves as they pass from one medium to another. Refraction, or the .Refraction definition: the change of direction of a ray of light, sound, heat, or the like, in passing obliquely from one medium into another in which its wave velocity is different.. See examples of REFRACTION used in a sentence.
Physics and Natural Law. . In refraction, a wave bends when it enters a medium through which it has a different speed. In diffraction, waves bend when they pass around small obstacles and spread out when they pass through small openings. In interference, when two waves meet, they can interfere constructively, creating a wave with larger .
Refraction is the bending of the path of a light wave as it passes across the boundary separating two media. Refraction is caused by the change in speed experienced by a wave when it changes medium. In Lesson 1, we learned that if a light wave passes from a medium in which it travels slow (relatively speaking) into a medium in which it travels fast, then the light wave would . In fact, the structure of an eye is fundamentally dictated by physics, and it has arisen separately by evolution somewhere between eight and 40 times, depending on which biologist you ask. . Many textbooks start with this as the definition of the index of refraction, although that approach makes the quantity's name somewhat of a mystery, and .
Snell’s Law: Refraction is governed by Snell’s Law, which relates the angles of incidence and refraction to the refractive indices of the two media involved.It is mathematically expressed as: 𝑛 1 × sin (𝜃 1)= 𝑛 2 × sin(𝜃 2). Where, 𝑛 1 and 𝑛 2 are the refractive indices of the first and second media respectively, and 𝜃 1 and 𝜃 2 are the angles of incidence and .This video tutorial lesson The Total Internal Reflection Video Tutorial discusses the nature of the reflection and refraction of light at the boundary. The discussion leads to an explanation of what total internal reflection is and when it occurs. Numerous graphics and . Explore the index of refraction: its definition, applications in technology and nature, challenges, and future potential in optics and physics. Understanding the Index of Refraction. The index of refraction, denoted as n, is a fundamental concept in optics and physics. It measures the extent to which light is bent, or refracted, when it passes .
For other materials such as glass the index of refraction becomes significant, \(n_{\text{glass}}=1.52\). Using ray representation refraction can be depicted as in the figure below, which depicts the same situation as in Figure 10.4.1, where light travels from a fast to a slow medium, or one with higher index of refraction to one with a lower .
The refractive index n of a medium (e.g., water, olive oil, etc.), also called the index of refraction, is defined as the quotient of the speed of light in vacuum c and the speed of light in the medium v.It is a dimensionless number that depends on the temperature of the medium and the wavelength of the light beam. In simple words, the index of refraction describes how fast a .
The speed of light c c size 12{c} {} not only affects refraction, it is one of the central concepts of Einstein’s theory of relativity. As the accuracy of the measurements of the speed of light were improved, c c size 12{c} {} was found not to depend on the velocity of the source or the observer. However, the speed of light does vary in a precise manner with the material it traverses.
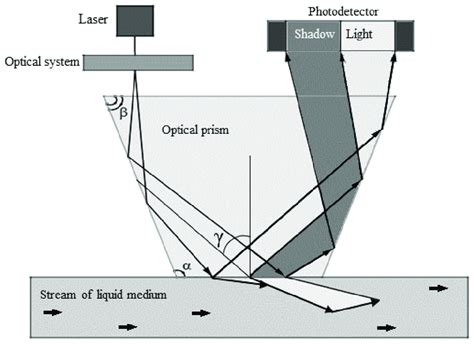
working principle of refractometer

webGELATO BORELLI, Blumenau - Comentários de Restaurantes & Fotos. Gelato Borelli, Blumenau: Veja dicas e avaliações imparciais de Gelato Borelli, com classificação Nº 5 de 5 no Tripadvisor e classificado como .
refractometer definition in physics|refractometer uses in laboratory